EITI at the International Open Data Conference
EITI at the International Open Data Conference
The International Open Data Conference (IODC) is the annual meeting of the global open data community. IODC aims to build stronger relationships between open data initiatives from different governments and establish a dialogue between policymakers, NGO’s and companies. Extractives were a key theme at this year’s IODC in Madrid.
The support for open government and open data continues to grow. Open data promotes accountability and good governance, enhances public debate and helps to combat corruption. Providing access to government data can empower individuals, the media, civil society and business to make better-informed choices about the services they receive and the standards they should expect. Open data can also be a valuable tool for government in improving policymaking and sector management. The EITI has been pursuing these objectives for over a decade, and the International Open Data Conference was an ideal opportunity to explore the links between our work and the wider open data community.
Extractives data dive
In advance of the main conference, the Natural Resource Governance Institute organised a two-day “data dive” with skill sharing sessions, presentations of data projects and discussions on new data tools and emerging trends in open data. A common theme was making better use of the data published by EITI implementing countries, and linking this data to other sources.

JUDS (Joined-up Data Standards)
JUDS (joined up data standards) are working on linking up different open data standards. More and more organisations are embracing Open Data, but this is often done without clear data standards. This limits the scope to utilise and cross-reference information, for example to detect gaps in disclosure.. The sankey chart below illustrates how EITI data links up with data from Resource Projects and Resource Contracts. In some cases, researchers can follow an extractive project by finding the contract on Resource Contracts, revenue information from the EITI and project level information from Resource Projects. The idea behind such flowcharts is to map the location and existence of several sources of data, and to enable a future automatic linking of such data for comparison and interoperability.
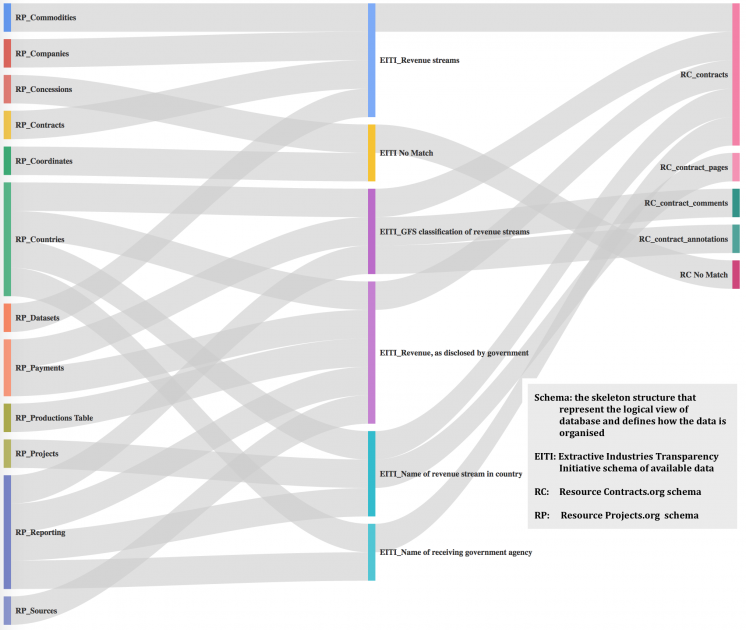
To find out more read JUDS open data conference blog.
Network mapping Nigeria EITI Beneficial Ownership data
All 51 EITI implementing countries are required to publish beneficial ownership (BO) disclosure roadmaps by 1 January 2017. BO information is complex and is often best visualised using a network mapper tool like the recently launched omodo platform. Open Oil have produced this network map displaying corporate and beneficial ownership published in the most recent Nigeria EITI Report Illustrating the corporate structures and complexities in a single image.
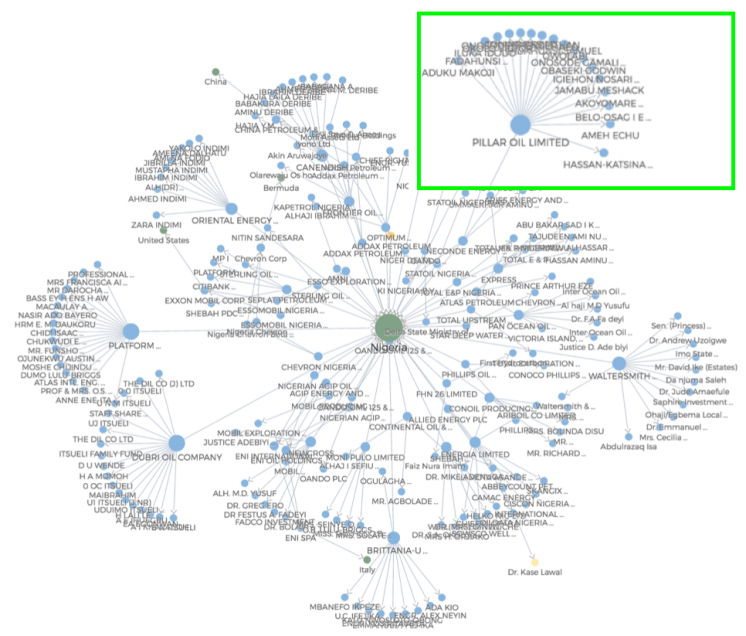
Why is beneficial ownership information important?
Extract-a-fact
US PWYP have created a Extract A Fact, a website directing users to different sources of information about the extractives in the US, including EITI data. Training videos explain how citizens can search, analyse and visualise the data. Extract-a-fact is still a beta site, meaning it is not finalised nor fully functional, and more content will be available when the SEC’s new reporting requirements come into force.
For more information on US PWYP’s extract-a-fact webpage and how to take advantage of this information, please visit. See the EITI's statement on mandatory disclosures and the SEC rulings for more information.
Mandatory disclosures and EITI Data interoperability
Laws that complement the disclosure requirements in the EITI Standard have been enacted in Canada, the European Union and the United States requiring disclosures of payments from extractive companies to governments. Open Oil has compared payment information released in accordance with the EU Directive with EITI data. There were discrepancies of less than 1% in some cases and much larger in others. There are several reasons that might be the case including differences in reporting standards and financial years. This again highlights the importance of open data standards. You can read more about Open Oil’s work here.
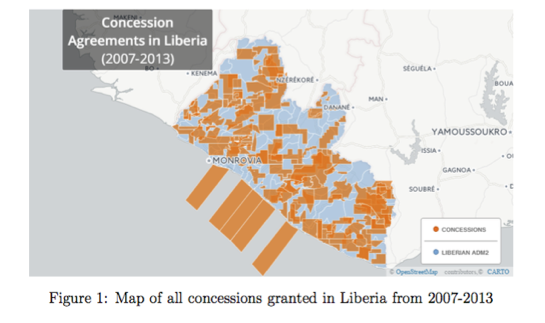
Mapping Liberia’s concessions data - AIDATA
'Along with other sources, EITI data was absolutely critical to unlocking the geospatial and temporal concessions data for Liberia.'
Jacob Sims, Aidata
Aidata has built a dataset of all known resource concessions granted in Liberia from 2004 to 2015 using open source data and three official sources: National Bureau of Concessions, the Ministry of Lands, Mines and Energy and the Liberian EITI (LEITI). Aidata plan to use this dataset in a number of innovative ways such as measuring the potential impact of concessions on local economic growth, conflict, social unrest, violence and deforestation.
Next steps
The EITI Board recently adopted an Open Data policy and new requirements for implementing countries. This includes a requirement that each country “agrees a clear policy on the access, release and re-use of EITI data”. Implementing countries are also “encouraged [to] publish EITI [data] under an open license, and to make users aware that information can be reused without prior consent”.
To find out more about how the International Secretariat is supporting implementing countries with this work read this blog.